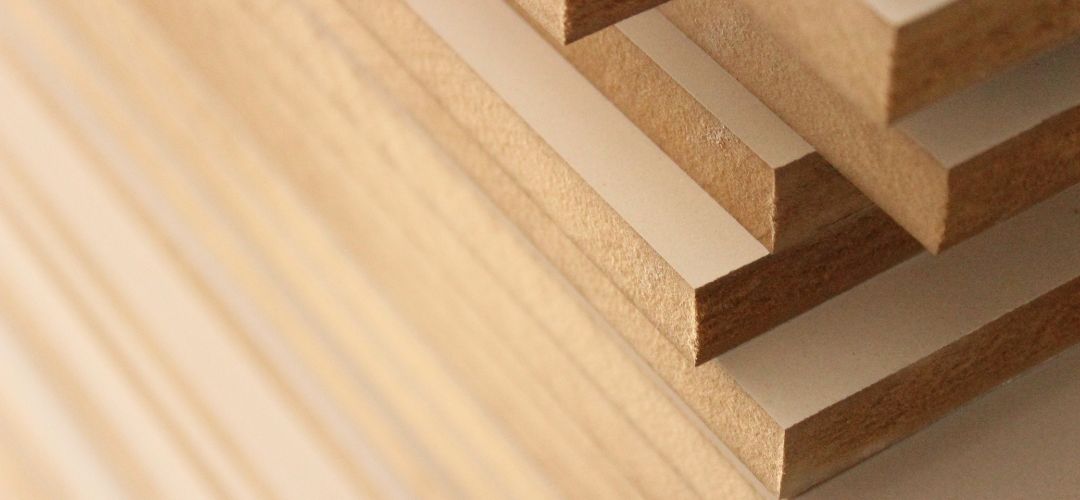
Plywood is a versatile and widely-used material in construction and furniture-making due to its strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It is made by gluing together thin layers of wood veneer, with the grain of each layer running at right angles to the next. This cross-graining technique gives plywood its strength and reduces the likelihood of splitting when nailed at the edges.
Types of Plywood
Softwood Plywood: Made from softwood trees like pine, cedar, and fir. It is commonly used in construction for walls, roofing, and flooring.Hardwood Plywood: Made from hardwood trees like oak, maple, and birch. It is often used in furniture-making and cabinetry due to its attractive appearance and strength.
Tropical Plywood: Made from mixed tropical woods. It is known for its superior strength and durability and is often used in marine applications and heavy-duty construction.
Flexible Plywood: Designed to bend and curve, making it ideal for projects requiring curved surfaces.
Fire-Retardant Plywood: Treated with fire-resistant chemicals, it is used in buildings where fire safety is a concern.
Pressure-Treated Plywood: Treated with chemicals to resist rot, decay, and insect damage, suitable for outdoor use.
Applications of Plywood
Construction: Used for subfloors, walls, roofs, and concrete formwork.Furniture: Popular for making shelves, cabinets, tables, and chairs.
Interior Design: Used for panelling, partitions, and decorative elements.
Marine Industry: Used for building boats and docks due to its resistance to water when treated appropriately.
Packaging: Employed in making crates and boxes for shipping.
Advantages of Plywood
Strength and Durability: Plywood is strong and can support heavy loads. The cross-graining process increases its strength.Versatility: Available in various sizes and thicknesses, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than solid wood while offering similar benefits.
Eco-Friendly: Plywood production uses less wood compared to solid wood products, making it a more sustainable choice.
Ease of Use: It can be easily cut, shaped, and finished with standard woodworking tools.
Choosing the Right Plywood
When selecting plywood for a project, consider the following factors:
Type of Plywood: Choose based on the specific requirements of your project, such as strength, appearance, and resistance to elements.Grade of Plywood: Plywood is graded based on the quality of the veneer and the presence of defects. Common grades include A, B, C, and D, with A being the highest quality.
Thickness: The thickness of plywood needed will depend on the load it needs to bear and the application.
Core Material: The core can be made of different materials like veneer, particleboard, or MDF, affecting the plywood's strength and weight.
Finish: Consider if the plywood will be visible or hidden. Choose a finish that suits your aesthetic requirements.
Why you select Best Plywood in India - Plywood remains a popular choice for builders, designers, and DIY enthusiasts due to its many advantages and wide range of applications hope you are looking for Plywood Company in Bangalore. Whether constructing a house, building furniture, or undertaking a creative project, plywood offers a reliable and versatile solution or Best Plywood for Wardrobe